In the wave of intelligent manufacturing,
Machine vision has become the core engine of industrial automation.
However, when faced with complex product shapes and materials,
❤️🔥The influence of reflections in optical imaging,
❤️🔥The interference of glares in optical imaging,
These have already severely affected the effect of visual imaging as well as the stability and accuracy of detection.
So, let's explore together today
How to deal with these troubles ❤️🔥.
At the same time,
It will provide you with a good idea for your vision solution,
Which can help you solve these problems.
Next, the cutting-edge technology that's about to make its appearance is
An seemingly ordinary optical element - the polarizing filter.

It is not only a "cutting-edge technology" for eliminating reflections, but also a crucial tool for improving detection accuracy and reducing the rate of false positives.
Before delving deep into the polarizing filter, let's first take a look at this:
01
What is a polarizing filter?
We call it the "reflection terminator" of machine vision.
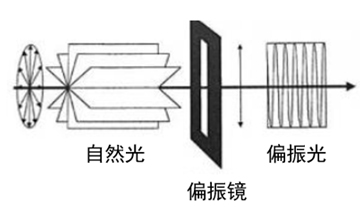
A polarizing filter (also known as a polarizer) is composed of two pieces of optical glass sandwiching a grid-like polarizing foil film. It only allows light parallel to the grid direction to pass through, completely blocks light in the perpendicular direction, and partially allows light at other angles to pass through.
Its core function is to weaken the polarized light reflection on the surface of objects.
02
Core principle
Its core technical principle is Brewster's angle, a term that may sound unfamiliar to you.
But it doesn't matter. Let me, the editor, study it together with you.
When natural light is reflected and refracted at the interface of a dielectric, generally, the reflected light and refracted light are partially polarized light. Only when the incident angle is a specific angle will the reflected light be linearly polarized light, and its vibration direction is perpendicular to the incident plane. This specific angle is called Brewster's angle or the polarization angle.
The remarkable feature of the polarizing filter is that by rotating its angle, it can precisely filter out the reflected light in this direction.
In industrial inspection applications, when the incident angle between the camera and the light source approaches Brewster's angle, the effect of the polarizing filter in eliminating reflections reaches its peak.
Therefore, the polarizing filter is particularly suitable for visual inspection of smooth surfaces such as glass, metal, and plastic.
03
Classification of Polarizing Filters
The polarizing filters commonly used in machine vision are divided into two categories: circular polarizing filters (CPL) and linear polarizing filters (PL).
Linear Polarized Light
When natural light passes through a polarizing device, only the polarized light in one direction can pass through this device, and then we obtain linear polarized light. The vibration direction of linear polarized light is determined.
Circular Polarized Light
The polarization direction of this kind of light rotates regularly. And the intensity of the light vector remains constant during the rotation process, that is, the light vector rotates along a circle, and this is circular polarized light.
After averaging over our observation time period, circular polarized light appears to be the same as natural light. However, the polarization direction of circular polarized light changes according to a certain rule, while the polarization direction of natural light changes randomly and without a pattern.
04
Application Scenarios
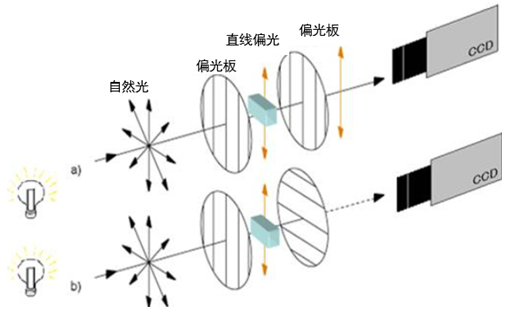
- Elimination of Specular Reflection
Case: Electronic Component Inspection
During the inspection of PCB boards, glass cover plates, or metal parts, surface reflection may lead to misjudgment of defects such as soldering joints and scratches. By rotating and adjusting the polarizing filter, more than 90% of the reflection can be eliminated, making micron-level defects clearly visible.
Case: Inspection of Pharmaceutical Aluminum Foil Packaging
The high reflection on the surface of the aluminum foil often conceals printed characters or sealing defects. The polarizing filter can darken the background, highlight the text and flaws, and improve the accuracy of OCR (Optical Character Recognition).
2. Enhancement of Color and Contrast
Case: Food Sorting
In the sorting of fruits and meats, the polarizing filter can reduce the reflection on the surface of the fruit peel and meat, making color analysis more accurate and reducing misclassification caused by light interference.
Case: Printing Quality Inspection
It eliminates the reflection of the ink, improves the color saturation, and reduces the algorithm's dependence on complex backgrounds.
Case: Sorting of High-Reflective Materials
Such as the detection of surface scratches on automotive parts and precision optical components.
In short, the application scenarios of the polarizing filter always revolve around situations involving reflection and glare. If you encounter such problems in your vision solutions, you can also start from this aspect.
05
Usage Methods and Optimization
- Combination of Light Source + Lens Polarizing Filter
Add a polarizing film in front of the light source to generate polarized light;
Add a CPL (Circular Polarizing Filter) in front of the lens and rotate it until the reflection is the weakest.
2. Exposure Compensation
Since the polarizing filter blocks about 3 to 4 stops of light, it is necessary to appropriately increase the exposure time or enhance the brightness of the light source.
3. Angle Adjustment
It is recommended to keep the angle between the camera and the light source at 30°-60°, which is close to Brewster's angle to enhance the effect.
06
Precautions
Although the polarizing filter has many advantages, it still cannot escape the law that too much of a good thing can be bad.
The following are some scenarios to avoid "overuse":
(1) Front-backlight Environment: When the light forms a 180° angle with the camera, there is very little polarized light, and the use of the polarizing filter is ineffective.
(2) Panoramic Stitching Inspection: Rotating the polarizing filter may lead to inconsistent color tones in the stitched images.
(3) Requirements for Special Optical Effects: The polarizing filter will weaken the texture of the light spot.
07
Currently, in the application of polarizing filters, many solution providers have implemented the innovative solution of dual-polarized light sources.
In the traditional solution, polarizing films need to be installed at both the lens and the light source ends. However, for the dual-polarized light source (such as the design by Hongyineng Technology), the polarizing film is integrated with the light source. By rotating the angle of the light source, the reflection can be eliminated, eliminating the need for a lens filter and simplifying installation and maintenance.
However, currently, it is not the optimal solution.
Perhaps, with the evolution and development of AI large models such as Deepseek, the intelligent integration of polarization technology:
The linkage of the polarizing filter, light source, and algorithm to achieve automatic polarization adjustment (such as automatically adjusting the angle by analyzing the reflection intensity in real time through AI) is the next direction worthy of in-depth study.
The polarizing filter is the "optical eye" of machine vision.
From eliminating reflection to enhancing color, it is an indispensable "optical tool" for us as machine vision engineers.
If you encounter reflection interference in your vision project?
Try using a polarizing filter first. Maybe it can solve your troubles!
|

